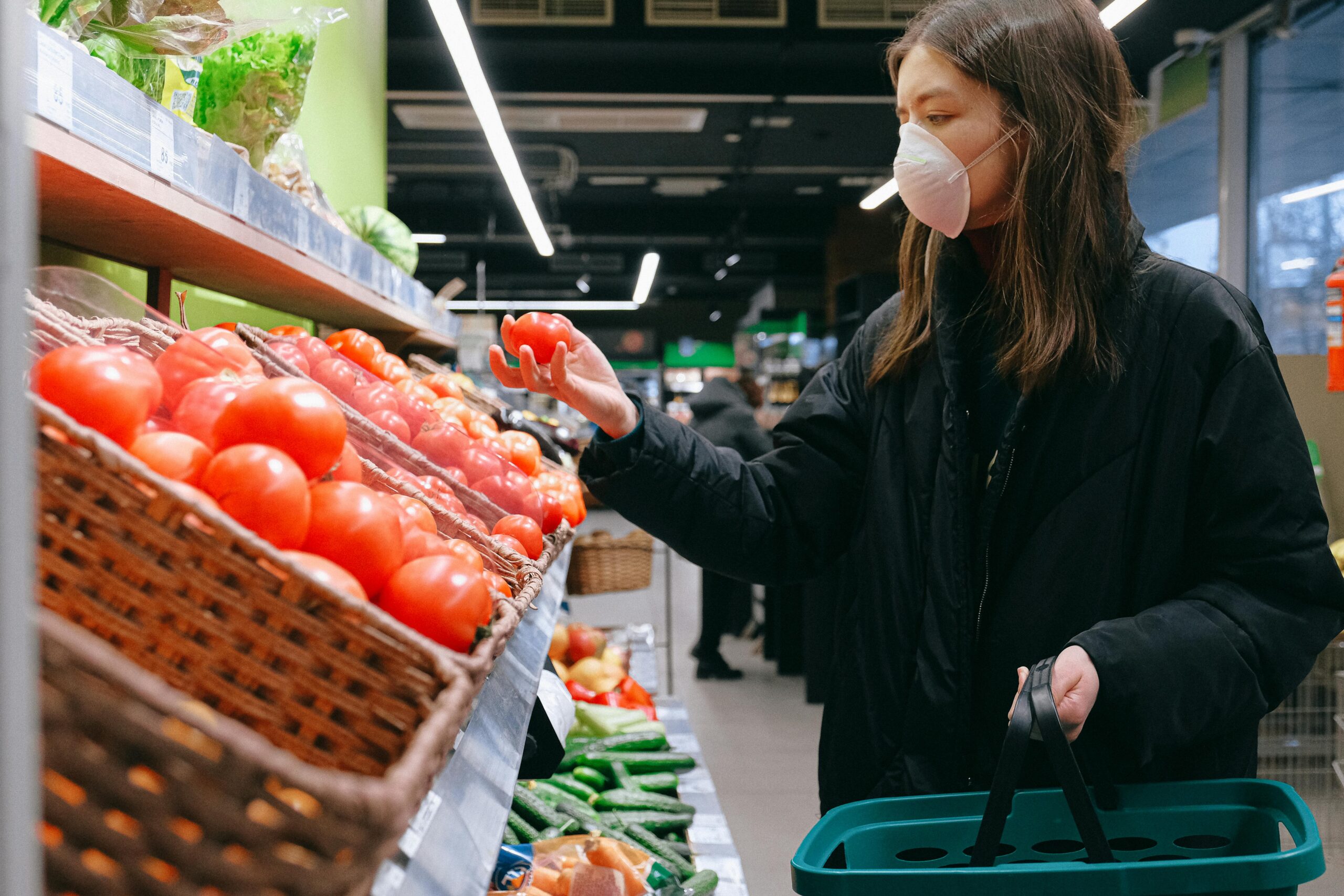
Areas of consumer protection The 2003 law aims to provide more excellent consumer protection by establishing individual state structures for its protection. The latter has recognized the right to appeal to consumer associations, the People’s Advocate, or in court when producers violate his rights. The development of the market economy, the signing of free trade with many countries in the region, private property, and numerous investments in various fields of the economy have been driving factors for the Albanian state to draft and adopt laws and bylaws the field of consumer protection. , constantly enriching them in the context of real changes in society. The legal framework for consumer protection includes several areas, such as:
-Water supply and treatment and disposal of wastewater;
An essential objective of the acts in this field is to guarantee and protect the public interests on the one hand and to create a transparent legal and regulatory environment that will encourage private investment in this sector. Drinking water and wastewater disposal are closely linked to protecting the health and quality of life of consumers.
- Viticulture, wine and other products derived from grapes;
The law aims to define and establish the basic rules for the functioning of viticulture, the production of grapes, wines, and other products derived from it, in the Republic of Albania. This act regulates all concepts related to grape by-products and the farmers’ obligations, domestic or foreign, operating in this field.
-Production and trade of tobacco and cigarettes;
The most important aspect of this law is the establishment and functioning of individual administrative structures, the National Agency for Tobacco – Cigarettes, and the Tobacco Fund, which inspects this process. These regulatory bodies should be more active, especially in protecting the life and health of smokers and non-smokers. This law is closely related to the law “On the protection of health from tobacco products”, which aims to protect public health from tobacco products and involuntary exposure to their smoke.
-Production, trade, and naming of olive oil;
The law defines the rules regarding the production, naming, and marketing of olive oil in the Republic of Albania, with origin and quality controlled by the international market’s requirements and standards. This law is in line with the United Nations Convention, where Albania adheres to these products and BIO products.
Electricity
The laws and bylaws in this field aim to provide conditions for the supply of electricity to consumers, according to standard parameters, through the efficient functioning of the electricity market and the development of competition in this sector, taking into account the protection of consumer interests, minimization of electricity service costs and its compatibility with the environment. Legislation in this area refers to the Civil Code for legal relations established, while this area is subject to regulation by the applicable law “On consumer protection”.
- Competition;Competition between traders is one of the areas directly related to state policies in favor of consumers. A competitive market, which operates with clear and well-defined rules, where products are offered by some traders, where monopolies on products are rare, where the state strikes cartels, enables the protection and realization of consumers’ economic and social interests offering them safe and diverse products.
-Medicines and pharmaceutical service;
This law has established the relevant state structures such as the National Center for Drug Control and the Drug Nomenclature Commission, which control drugs and inspect entities operating in the pharmaceutical field. A new, fundamental structure that aims to protect the consumer from the unwanted and harmful effects of drugs is the Center of Pharmacological marketing and processing of milk and milk-based products; The purpose of this law is to guarantee consumer safety for milk and milk-based products, aiming at the production and marketing of these quality products, according to the requirements and standards of the internal and external market, through licensing and control of production farms, milk collection, and processing.
-Banking system;
This law provides initial consumer protection about banking services. Thus, in the sense of this law, the client is the person who is a user of banking and financial services. Consumer loans are one of the most sensitive consumer contracts nowadays. The obligation of financial institutions to inform consumers about their rights and responsibilities in the pre-contractual and contractual phase is almost not fulfilled, or the information provided is inferior and does not meet legal requirements.
- Safety and conformity of non-food products; This law defines the rights and obligations of producers and distributors to place safe products for consumers in the Albanian market, excluding the scope of application products regulated by special laws. It provides for the duties, responsibilities, organization, and cooperation of the structures responsible for market surveillance. The new act, of 2011, together with the amendments of 2013, aims to approximate the Albanian legal framework regarding non-food products with directive no. 2001/95 / EC of the European Parliament and the Council, 3 December 2001 “On general product safety”; with Regulation no. 765/2008 / EC of the European Parliament and the Council, dated 9 July 2008 “On the establishment of requirements for accreditation and market surveillance about the marketing of products”, which repeals Regulation no. 339/93 / EEC.
In everyday life, every action we perform as individuals, related to the purchase or use of products or services, to meet personal needs, defines our role as consumers. For this reason, the above list is not exhaustive; on the contrary, there are still many acts that regulate the field of consumer protection.
Another fundamental law, which is in the footsteps of the community legislator and transposed several communities acts, is the law “On trade and market surveillance non-food products.” This law stipulates the general principles for placing on the market of non-food products, which are not regulated by a particular law, specifies the obligations of producers and other entities to put on the market safe products and defines the structures responsible for supervising market and their competencies.